From the Start Menu select:
Start -> All Programs -> Accessories -> Command Prompt
At the prompt, type telnet and hit enter. The telnet client will appear.
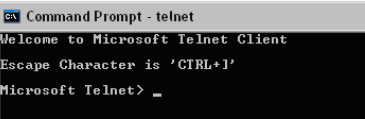
Figure 1: Type “telnet” and hit Enter
At the prompt type o <ip address> <telnet port>. The default telnet port is 9999.
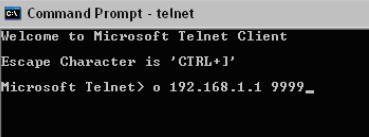
Figure 2: Proceed in Command Prompt
A password prompt, or device menu should appear. This means it’s possible to communicate to the device via telnet.
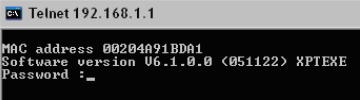
Figure 3: Password Prompt
If communication times out, it won’t be possible to communicate to the device via telnet. A few things to check:
1. Make sure the 5100-iSIC is powered and the Ethernet cable is plugged into its internet connection.
2. Check the router/switch status lights to make sure the Ethernet cable plugged in from the 5100-iSIC has a connection to the internet.
3. Check to see if the default port has changed from 9999. If unsure, try running the device installer program as described earlier in this manual to detect the device.
Note: this must be done when connected to the same subnet as the 5100-iSIC.
4. If connecting from a remote network, make sure the router the 5100-iSIC is connected to has a static IP address and correctly port forwards the correct telnet port and 5100-iSIC
address.
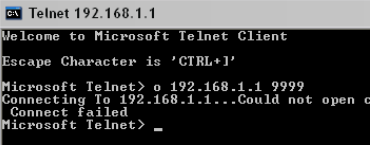
Figure 4: Example Timeout
After connecting to the device using telnet, the default settings can be adjusted. The settings that can be manually changed are the port number the data logger uses, etc. Be sure to leave the Baud rate at the same baud rate the data logger is configured for (default is 9600).
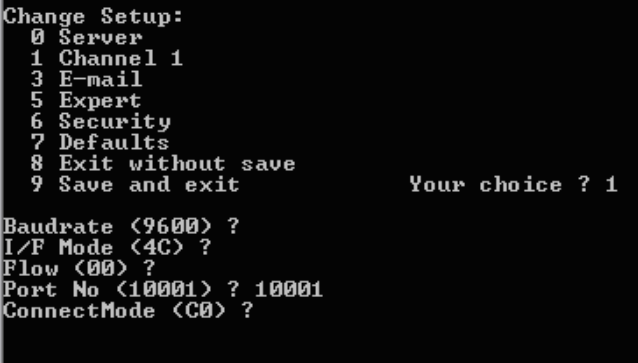
Figure 5: Options for Changing Setup in Command Prompt
REV: 13G17
